You have to must know about robot !
What Is Robot?
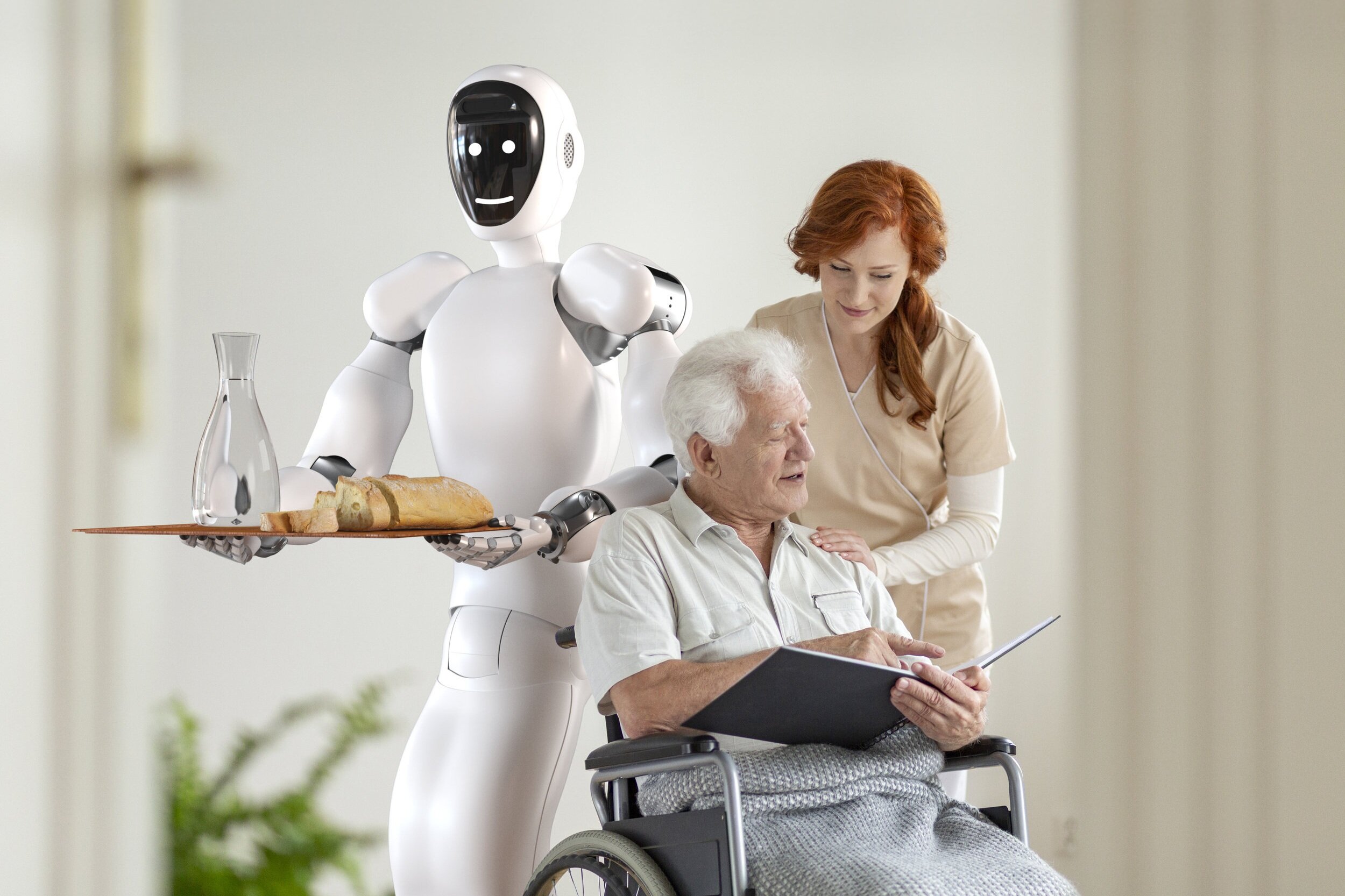
A robot is a machine programmed to perform tasks automatically, often mimicking human actions or replacing repetitive human tasks. Robots can come in various forms and serve diverse purposes, from industrial robots used in manufacturing to autonomous robots in exploration or household robots like vacuum cleaners. They typically consist of sensors, actuators, a power source, and a control system that guides their actions.
 |
| Robot |
Robots can be controlled remotely by humans or function autonomously through artificial intelligence and sensors.
How To Robot Work ?
Robots work through a combination of hardware components and software programs that enable them to perform specific tasks or functions. Here's a general overview of how robots work:
1. Sensors: Robots have various sensors that gather information about their environment. These sensors can include cameras, infrared sensors, ultrasonic sensors, gyroscopes, accelerometers, etc.
 |
| Robot Sensor |
These sensors help the robot perceive and understand its surroundings.
2. Processing and Control System: The sensory information collected by the robot is processed by its control system, which can consist of microprocessors or a more sophisticated AI-driven system. This system interprets the data from sensors and makes decisions based on programmed algorithms or AI models.
3. Actuators and Effectors:Once the control system has processed the information and made decisions, it sends commands to actuators or effectors. Actuators are the mechanical components of the robot responsible for carrying out physical actions. These could be motors, wheels, arms, grippers, or other mechanisms that enable movement or manipulation.
4. Execution of Tasks:Based on the information received from sensors and the decisions made by the control system, the actuators perform the necessary actions to accomplish the robot's task or objective. For instance, a robotic arm in a manufacturing setting might pick up items and place them in specific locations on an assembly line.
5. Feedback Loop: Some robots have feedback mechanisms that allow them to adjust their actions based on new information received from sensors during the task execution. This feedback loop helps the robot adapt to changing conditions and improve its performance.
6. Power Source:Robots require a power source to operate, which could be batteries, electrical outlets, or other sources of energy, depending on the type and application of the robot.
Overall, robots work by integrating sensory inputs with processing capabilities and physical actions to perform tasks efficiently and accurately. Their functionality can range from simple repetitive tasks to complex actions driven by advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms.
What for Robot used for ?
Robots are used across various industries and for a multitude of purposes due to their versatility and ability to perform tasks more efficiently than humans in certain scenarios. Some common uses of robots include:
1. Manufacturing: Industrial robots are extensively used in manufacturing and assembly lines for tasks like welding, painting, assembling components, packaging, and quality control. They increase productivity and precision while reducing production costs.
2. Healthcare: Robots assist in surgeries, rehabilitation, and caregiving. Surgical robots enable minimally invasive procedures with greater precision, while robots in rehabilitation aid patients in regaining mobility and strength.
3. Logistics and Warehousing: Robots are employed in warehouses for tasks like inventory management, picking and packing items, and transportation of goods. Autonomous mobile robots navigate warehouses efficiently, improving logistics operations.
4. Agriculture:Agricultural robots perform tasks such as planting, harvesting, and monitoring crop health. They can increase crop yield, optimize resource use, and reduce manual labor.
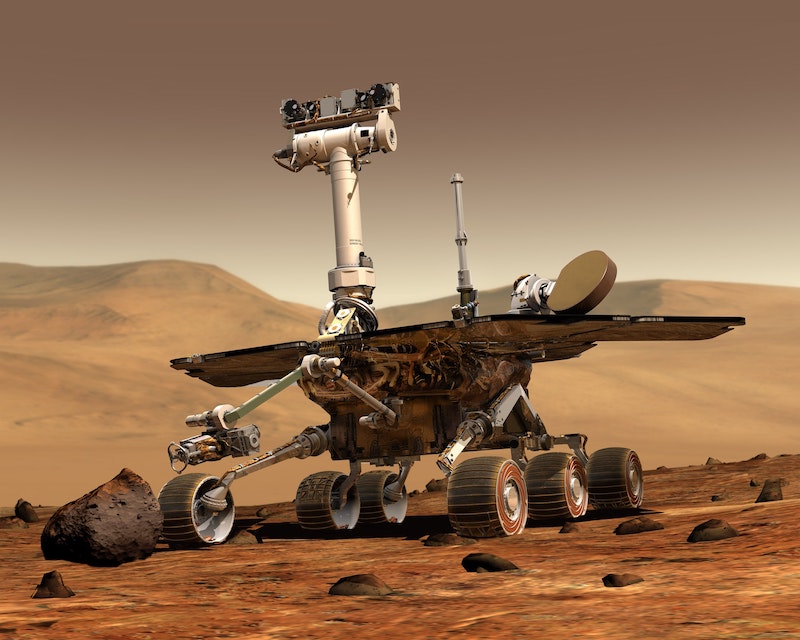
5. Exploration and Research: Robots, including rovers and drones, are used in exploration, both in space and underwater, to collect data, conduct experiments, and gather information in environments that are hazardous or inaccessible to humans.
6.Domestic Tasks: Household robots like robotic vacuum cleaners, lawn mowers, and smart assistants simplify chores and improve convenience in homes.
7. Education and Research: Educational robots are used in schools and universities to teach programming, robotics, and STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) concepts. Research robots assist scientists in conducting experiments and gathering data.
8. Entertainment: Robots are used for entertainment purposes in theme parks, museums, and interactive exhibits. They can serve as interactive guides or performers, enhancing visitor experiences.
9.Defense and Security: Military robots are employed for surveillance, bomb disposal, reconnaissance, and in some cases, combat situations to reduce risks to human personnel.
10. Service Industry: Robots are being introduced in the service industry, such as in hospitality for tasks like room service delivery or customer assistance.
The applications of robots continue to expand as technology advances, enabling them to perform increasingly complex tasks across various domains, making them an integral part of modern-day industries and daily life.
why robot harm for human evolution
The potential harm of robots to human evolution is a complex topic that involves ethical, social, and technological considerations. Here are some aspects to consider:
1. Job Displacement: One concern is that automation and robotics could lead to job displacement, potentially causing economic disruptions and impacting livelihoods. As robots take over certain tasks, humans might need to adapt by acquiring new skills to remain employable.
2.Dependency and Overreliance: Overdependence on robots and automation could diminish certain skills or abilities in humans. If people rely heavily on technology for essential tasks, they might lose proficiency in those areas themselves, affecting their ability to function without technological assistance.
3.Ethical Concerns: There are ethical considerations regarding the use of robots, especially in fields like military robotics or autonomous decision-making. Issues related to accountability, biases in algorithms, and the ethical implications of robots making critical decisions are significant concerns.
4. Social Interaction:Increased interaction with robots might alter social dynamics. If robots become prevalent in caregiving or companionship roles, there could be impacts on human-to-human relationships and social skills development, particularly in vulnerable populations like the elderly or children.
5. Inequality and Access: The deployment of advanced robotics could widen the gap between those who have access to technology and those who don't. Socioeconomic disparities might increase if certain populations or regions lack access to technological advancements.
However, it's important to note that the potential harm caused by robots is not inherent to the technology itself but often arises from how it's developed, deployed, and regulated. Regulations, ethical guidelines, and thoughtful integration of robotics into society can mitigate many of these concerns and ensure that the evolution of humans is positively impacted by technological advancements rather than hindered by them. Additionally, advancements in robotics and automation have the potential to improve human lives significantly by alleviating mundane tasks, enhancing productivity, and enabling breakthroughs in various fields, contributing positively to human evolution.
Robot FAQs
1. What is a robot?
A robot is a machine programmed to perform tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously. It can be equipped with sensors, actuators, and a control system to interact with its environment and carry out specific functions.
2. What are the types of robots?
There are various types of robots, including industrial robots used in manufacturing, humanoid robots designed to resemble humans, autonomous drones for aerial tasks, collaborative robots (cobots) that work alongside humans, and more specialized robots for specific applications like medical surgeries or exploration.
3. How do robots work?
Robots work by receiving input from sensors, processing that information via a control system (usually through algorithms or AI), and then using actuators to perform physical actions or tasks based on the processed data.
4. What are robots used for?
Robots have diverse applications across industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, logistics, exploration, education, entertainment, defense, and service industries. They perform tasks ranging from assembly line work to surgeries, from crop harvesting to space exploration.
5. Are robots replacing humans in jobs?
Automation and robotics have led to some job displacement in certain industries. Routine and repetitive tasks are more susceptible to being automated, but the introduction of robots also creates new job opportunities in fields related to robotics, AI, maintenance, and programming.
6. What are the ethical concerns about robots?
Ethical concerns regarding robots include issues of job displacement, potential biases in AI algorithms, the use of robots in military applications, privacy concerns with advanced surveillance, and the ethical implications of robots making critical decisions.
7. Can robots learn?
Yes, robots can learn through various techniques, including machine learning and artificial intelligence. They can adapt to new situations, improve their performance based on feedback, and even develop new capabilities over time.
8. How safe are robots to interact with humans?
Safety measures are integral in robot design, especially for collaborative robots meant to work alongside humans. Safety features include sensors that detect human presence, compliance with safety standards, and programming to avoid causing harm during interactions.
9. What is the future of robotics?
The future of robotics involves further advancements in AI, machine learning, and sensory capabilities. Robots are expected to become more autonomous, adaptable, and capable of handling complex tasks across various industries while maintaining safety and ethical standards.
10. How can I get involved in robotics?
You can get involved in robotics through education in STEM fields (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics), participating in robotics clubs or competitions, pursuing degrees or certifications in robotics, or exploring online resources and tutorials for learning robotics programming and development.