What is the process of LCD panel ?
What is the process of LD panel ?
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) panels are the technological backbone of many modern screens, from TVs to computer monitors and smartphones. Their operation involves a sophisticated interplay of components and principles that result in vibrant, colorful images. Here's an overview of how "LCD" panels work:
 |
| LCD display |
Basic Structure:
An "LCD" panel consists of several layers that work together to produce images. At its core, it comprises two polarized glass sheets with a layer of liquid crystal material between them. The liquid crystals align between these sheets, and the manipulation of these crystals creates the display's images.
Liquid Crystals:
The liquid crystal material in an "LCD" panel doesn't behave like a typical liquid or solid. Instead, it is a unique state of matter that can flow like a liquid while maintaining some crystalline properties. These crystals react to electrical currents and change their orientation when voltage is applied.
Polarization and Light Control:
Polarizing filters on the glass sheets allow or block light based on their orientation. When light passes through the first polarizing filter, it aligns in a specific direction. Then, it encounters the liquid crystal layer, where electrical currents control the alignment of the crystals. The alignment of the crystals determines whether light can pass through or gets blocked by the second polarizing filter.
Pixel Formation:
Each pixel on an "LCD" panel consists of three sub-pixels – red, green, and blue – which combine to create a wide spectrum of colors. The liquid crystals in front of each sub-pixel can twist or remain straight based on the electrical charge received. This manipulation allows varying degrees of light to pass through each sub-pixel, contributing to the final color and intensity of the displayed image.
.webp) |
| Pixel: Red, Green, Blue |
Active Matrix and TFT Technology:
Most modern "LCDs" use "Thin-Film Transistor (TFT) technology", which incorporates a transistor for each pixel. This setup, known as an active matrix display, enables precise control over each pixel. The transistors help maintain the required charge on the liquid crystals for a stable image without distortion or flickering.
 |
| TFT display |
Backlighting:
"LCD" panels require a light source to illuminate the images they produce. Typically, a cold cathode fluorescent lamp (CCFL) or Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) positioned behind the panel provide this backlight. The light passes through the liquid crystal layer, and the manipulation of the crystals determines how much light passes through, resulting in the display of different colors and shades.
 |
| Backlighting |
Color and Image Quality:
The quality of images displayed on an LCD panel depends on various factors, including the alignment and quality of the liquid crystals, the accuracy of the color filters, the efficiency of the backlighting, and the resolution of the display.
 |
| Color Gradints |
Advantages and Limitations:
LCD panels offer several advantages, such as energy efficiency, thin profile, and the ability to produce sharp images. However, they may have limitations like limited viewing angles and potential issues such as response time and color accuracy, which newer technologies like OLED aim to address.
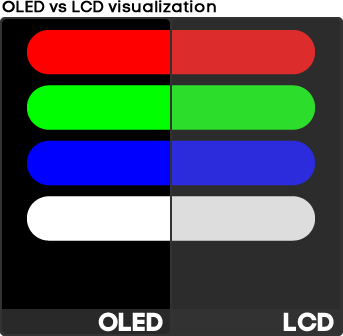 |
| Oled Vs Lcd Panel |
In conclusion, the complex interaction between liquid crystals, polarizing filters, transistors, and backlighting allows LCD panels to create the vibrant and detailed images we see on screens across various devices, making them an integral part of modern technology.
